The Rise of Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles: Pros and Cons
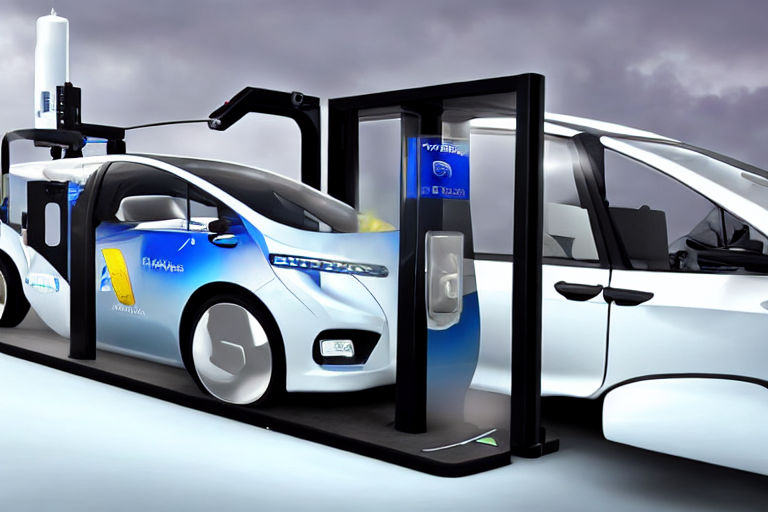
Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) have been gaining popularity in recent years as an alternative to traditional gasoline-powered cars. FCVs are electric vehicles that use hydrogen as their fuel source and produce only water as a byproduct.
Pros of Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles
- Zero Emissions: FCVs emit only water vapor as their byproduct, making them much cleaner than traditional gasoline-powered cars. This makes them an appealing option for environmentally-conscious consumers.
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: FCVs are more fuel-efficient than traditional gasoline-powered cars, which means lower fuel costs for drivers.
- No Noise Pollution: FCVs run more quietly than traditional cars, reducing noise pollution in urban areas.
- Fast Refueling: Refueling a FCV is similar to refueling a traditional car and takes only a few minutes, making it a convenient option for drivers.
Cons of Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles
- Lack of Infrastructure: One of the biggest barriers to widespread adoption of FCVs is the lack of hydrogen refueling stations. Currently, there are only a few dozen hydrogen refueling stations in the United States, making it difficult for drivers to find a place to refuel.
- High Cost: FCVs are currently more expensive than traditional gasoline-powered cars, making them less accessible to many consumers.
- Complex Technology: FCVs require a complex system of components, including a fuel cell stack, hydrogen storage tank, and electric motor. This makes them more difficult to manufacture and repair than traditional cars.
- Limited Range: FCVs have a shorter range than traditional cars, typically around 300 miles per tank compared to 400-500 miles for gasoline-powered cars. This makes them less practical for long road trips.
Conclusion
Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles offer several advantages over traditional gasoline-powered cars, including zero emissions, improved fuel efficiency, quiet operation, and fast refueling. However, they also face several challenges, including a lack of infrastructure, high cost, complex technology, and limited range. As hydrogen fuel cell technology continues to develop and infrastructure expands, these challenges may be overcome and FCVs could become a more viable option for drivers seeking a cleaner and more efficient vehicle.